ElasticSearch - Now you Know
All enterprise application are just a wrapper service that gets evolved gradually , but underneath there lies basic functions. Here, I’ll start with a simple DSA question where we add sentences and search it by some input words.
The algorithm that we are using is exploits the concept called InvertedIndex and the elasticsearch uses ApacheLucene The following code gives a gist the undergoing logic.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Doc
{
int id;
string data;
};
class ElasticSearch
{
public:
unordered_map<string, vector<Doc> > invertedIndex;
ElasticSearch()
{
}
void add(Doc *d)
{
vector<string> characters = analyzeAndTokenize(d->data);
for(auto a: characters)
{
// cout<<a;
// cout<<endl<<d->data;
invertedIndex[a].push_back(*d);
// // docmap[d.id]=d.data;
}
}
vector<string> analyzeAndTokenize(string word)
{
return {"Nafis" , "I" , "am"};
//hard coded, you can add a split function
}
void Search(string word)
{
vector<Doc> docs;
for(auto a: invertedIndex)
{
if(a.first==word)
{
docs = invertedIndex[word];
break;
}
}
for(auto a : docs)
{
cout<<a.data;
}
}
};
int main()
{
ElasticSearch *e = new ElasticSearch();
Doc *d = new Doc();
d->id=1;
d->data="Hey I am Nafis, Find Me";
e->add(d);
e->Search("Nafis");
}
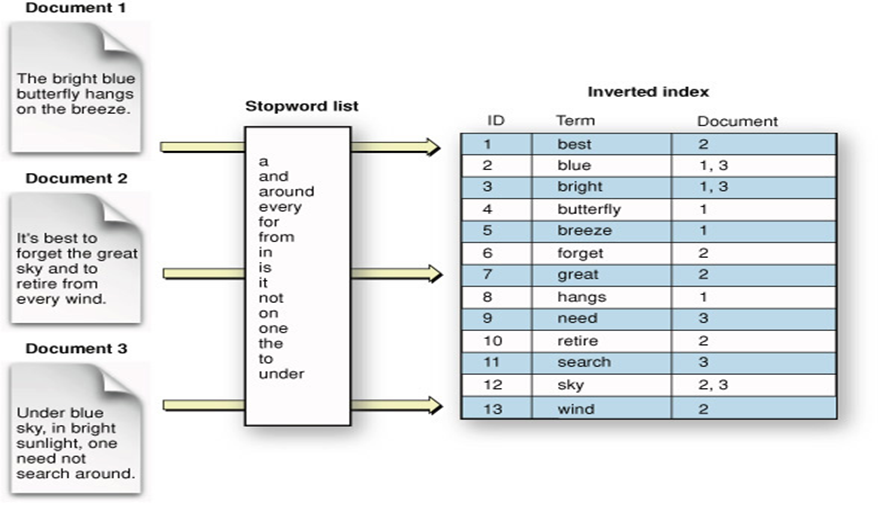
Lets Start
Ohk, now after the DSA round, you are hired. We cant just have this, we need to provide a conventional way to developers to utilise these functions.
Oooh, meta programming!!
Its there, but we all know, what happen, we developers play around with reflections.
So, the PM comes with a solution to standardize it. Its time to get the sprint board ready.
Voila!! Apache community did a commendable job to expose these logic through api. Now, all we have to learn is the schema and standard operations to manipulate default behaviour.
Operations:
Create index
PUT /index
Lets be typesafe [Mapping]
Hey All JavaScript developers who are migrating to typescript. We know, we can use “any” type but should we?
Com’on , just for the sake of avoiding runtime error, please specify the type. But, this doesnt mean, elasticSearch need your help , its self-sufficient to dynamically set the type.
PUT /my_index/_mapping?pretty
{
"properties": {
"email": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
Get the analyzer
As earlier, you saw a analyzer function, we can replicated that too using some call. You just have to make a few call and it will break it into pieces.
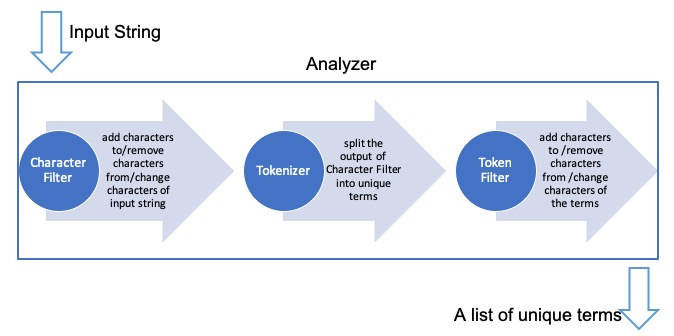
Request
PUT my-index-000001
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_custom_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "standard",
"char_filter": [
"html_strip"
],
"filter": [
"lowercase",
"asciifolding"
]
}
}
}
}
}
POST my-index-000001/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "my_custom_analyzer",
"text": "Is this <b>déjà vu</b>?"
}
How to boost and set Score
Apologies to keep you waiting, we’ll get to search , but please let me know your preference. I know you like to meet your colleague but you are also enjoying the work from home.
So, if someone ask, you have to choose. But How? I love WFH 3000 , so we have the answer.
Individual fields can be boosted as we wish — count more towards the relevance score — at query time, with the boost parameter as follows:
PUT my-index-000001
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"boost": 2
},
"content": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
Wait!! What is relevance score. There is a mathematical formula for getting the relevance score.. To understand and tweak the relevance score, there is a _explain api . I dont want to say it again. Just make a call. Commnication helps relationship.
GET /my-index-000001/_explain/0
{
"query" : {
"match" : { "message" : "elasticsearch" }
}
}
Aha , we can scale
ElasticSearch mm se cm ban gaya hy. Ab chahiye, full izzat.
For handling huge request volumes , elasticsearch embraced the standard Distributive System concepts and provided with configurable setup to scalable search engine.
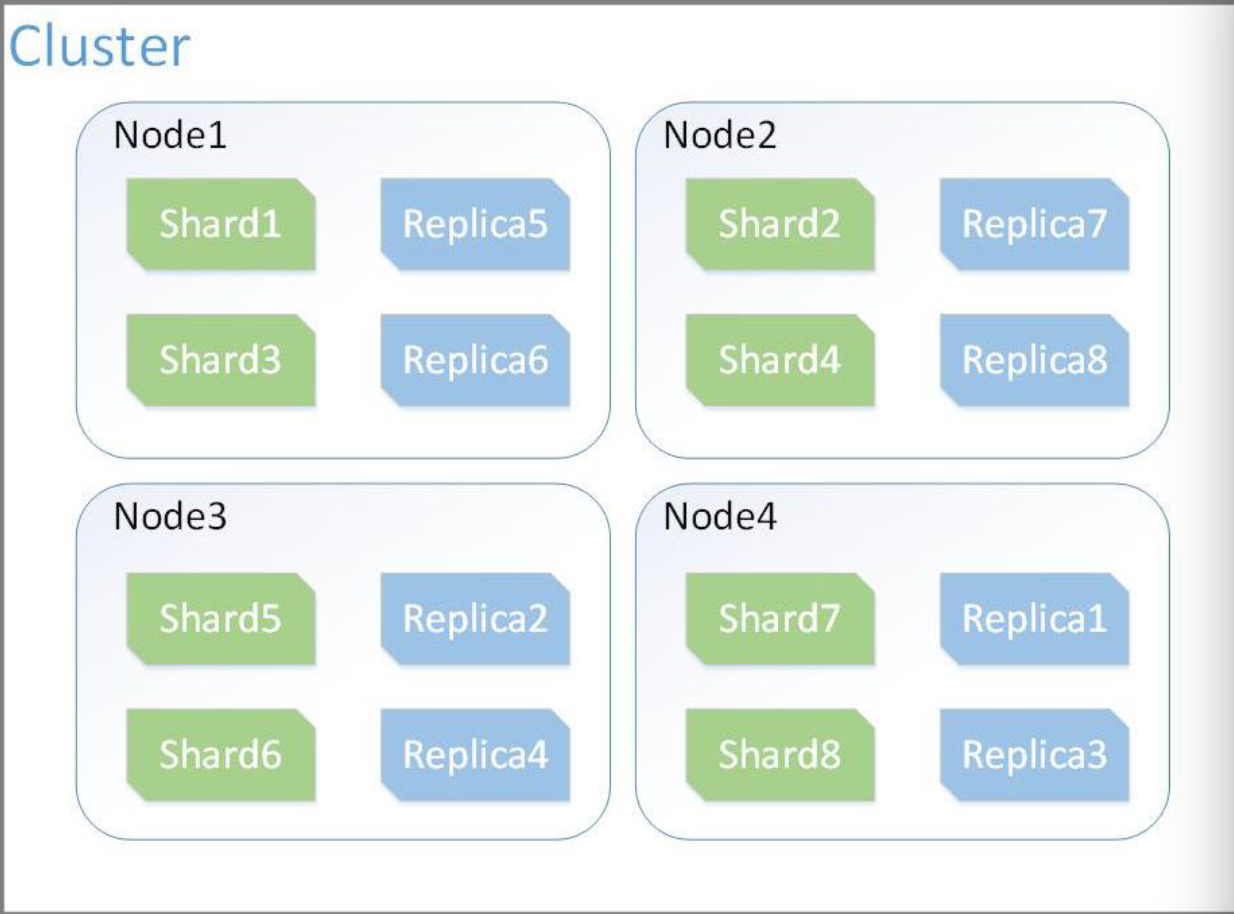
The ElasticSearch distributive architecture is configurable and can be orchestrated through config files We can specify our own routing parameters and customise our indexing. The default formula is : shard = hash(routing) % number_of_primary_shards
PUT my-index-000001/_doc/1?routing=user1&refresh=true
{
"title": "This is a document"
}
GET my-index-000001/_doc/1?routing=user1

